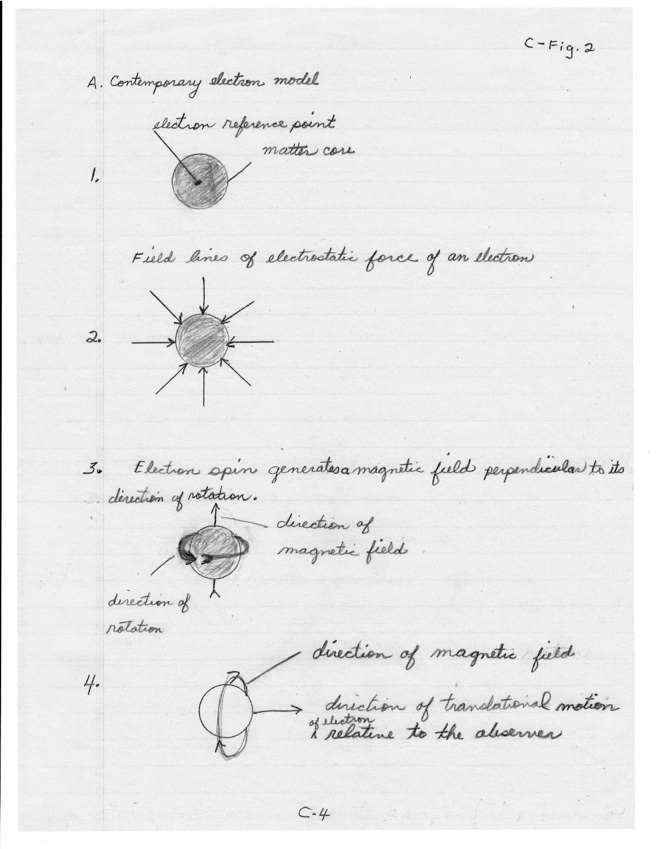

C-Fig. 2. Comparisons of the COM and Contemporary Models for the Electron.
A. The contemporary electron model. The electron represents a locus with which the properties of mass, electrostatic force, intrinsic spin, and a magnetic force have been associated.
1. Representing the mass component as a sphere, a “visual” model for an isolated electron has been fabricated.
-
2. The associated electrostatic field of an electron is represented by directional lines. By convention, lines are directed toward the negative charge of the electron.
-
3. As a result of its intrinsic spin the electron generates a magnetic field oriented perpendicular to the direction of its rotation. Arrow indicates the direction for a magnetic field.
4. In accelerated translational motion “relative to the observer” the electron manifests a circular magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of translational motion.
